The challenge
Farming contributes to a wide range of global challenges. It can also be the solution.
However, there are barriers that prevent farmers becoming drivers of positive change. These include:
- Knowledge and understanding
- Measurement and monitoring
- Systemic and structural

The solution
The GFM tackles key barriers to sustainable farming by creating a shared language, facilitating practical ways to measure outcomes and establishing a framework that aligns the farming system.
It has the power to connect farmers, supply chains and policymakers through shared sustainability goals and consistent, whole-farm data. By focusing on outcomes that matter to everyone, the GFM supports more joined-up action and drives long-term, system-wide change.

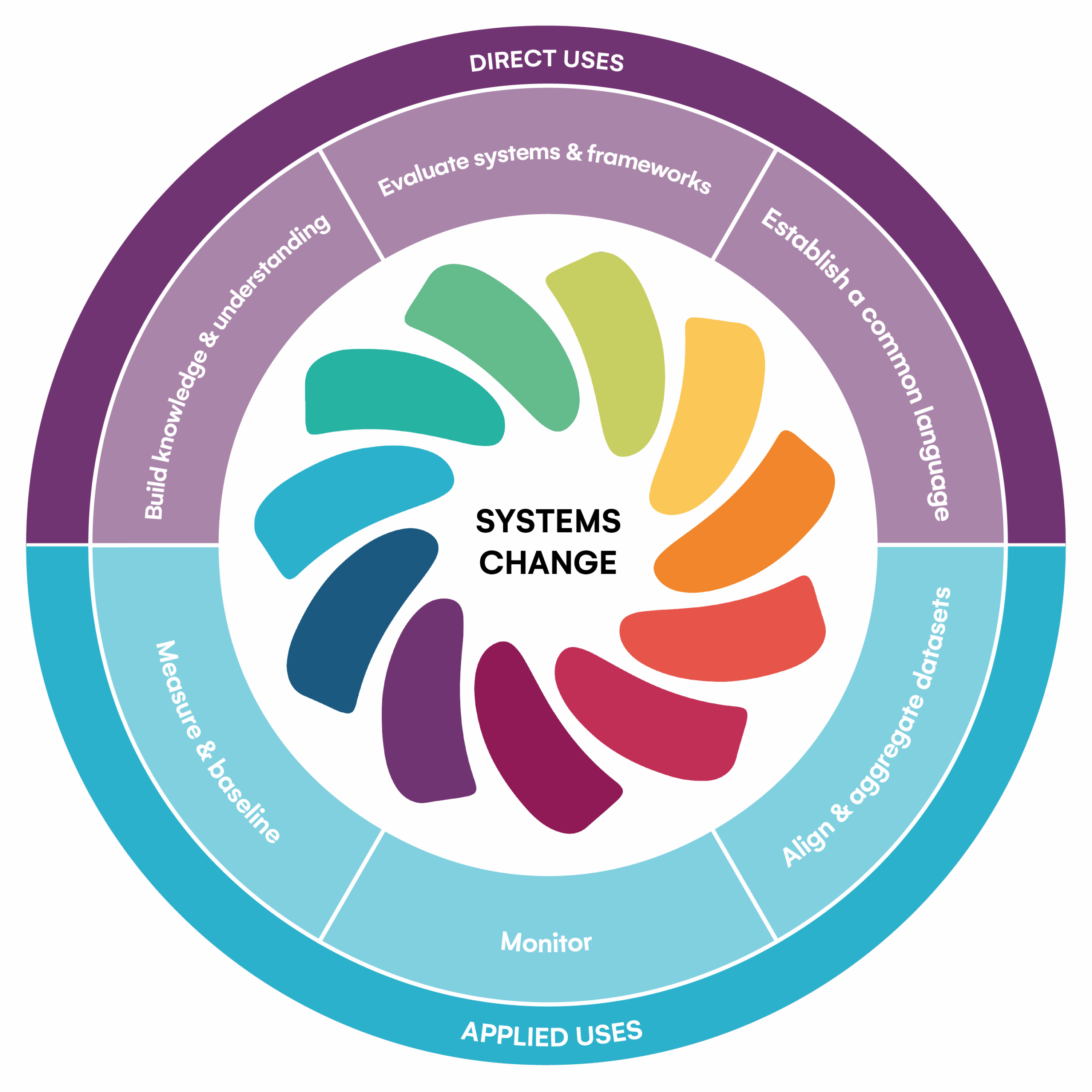
Using the GFM
The GFM can be used directly to define farm-level sustainability, align understanding and establish a common language. It can also be applied into existing infrastructure to enable holistic measurement and align data collection.
Together, these approaches drive systems change.
Key features
Global Farm Metric
Holistic
Covers social, economic and environmental dimensions of the farm, recognising synergies and multi-stakeholder perspectives.
Aligned
Can be embedded within assessments, tools and frameworks, creating a common language to drive consistency and collaboration
Practical
Can underpin primary data collection that is useful and relevant at farm-level
Outcomes-based
Identifies shared goals across the farming industry and the indicators to monitor progress towards them
Inclusive
Inclusive of and applicable to all farming systems and landscapes
Evidence-based and evolving
Developed from farm trials and scientific research
Drives change
Enables collective action for nature, climate and people